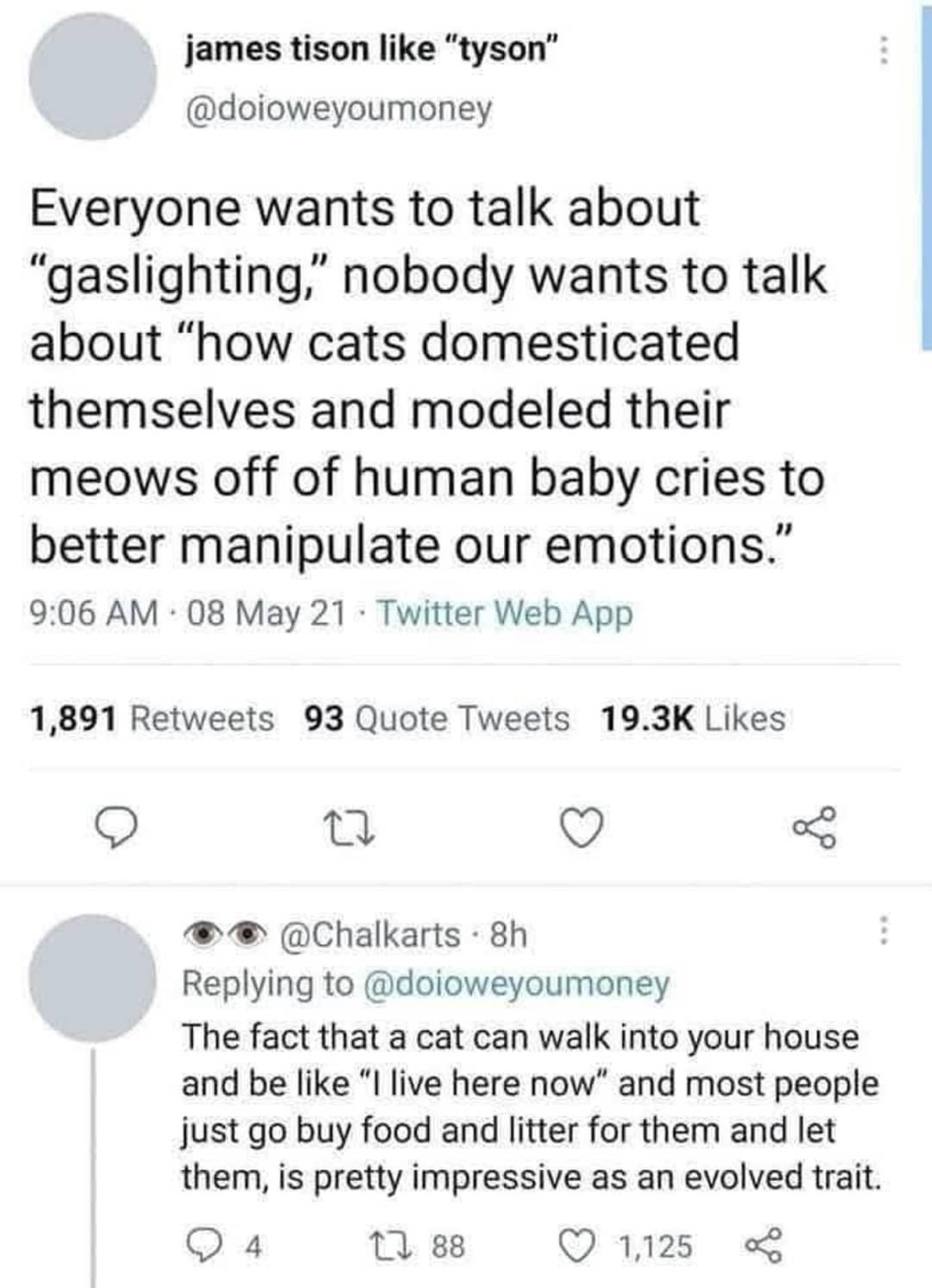
I don't know about that human baby thing.
Science Memes
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
This is a science community. We use the Dawkins definition of meme.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !reptiles and [email protected]
Physical Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !self [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Memes
Miscellaneous
IIRC, it's more that they over time figure out what sounds and actions get their owner's attention. We respond better, unconsiously or otherwise when they meow at us.
My old cat figured out, before I did, that if she knocks shit off the coffee table I get up and check if her bowl is empty.
Generally wild/feral adult cats are more or less mute outside of anger/mating/territory calls, but domesticated cats keep their kitten vocalizations if we respond to them.
My current cat is very vocal and we responded playfully to his meowing as he grew up.
Edit: Here's a scientific american blog/article about it. I don't think it's something we have confirmation on, just a good hunch.
it's literally just that cats figure out that making noise draws our attention, and even better if they make a cute noise.
Yeah that seems really far fetched. Humans are generally bad at communicating with mostly body posture and scent. We have no tail to wiggle, no easily movable ears and no chance to use cat pheromones.
So naturally the cat has the best chance to get a response by using vocalication/sounds. It is just coincidence that their kittens do also mostly respond to sounds in their first weeks.
The resemblance to baby vocalizations can be rather unsettling with some cats. I suppose it's somewhat natural since they're about the same size as a newborn human, but specifically adopting somewhat human-like (and thus baby-like, because that's the one they can imitate the best) vocalization doesn't seem that far-fetched.
I mean, I'm not sure cats are out there observing human babies and intentionally imitating them. They have pattern recognition machines in their heads just like we do. "Make noise = human pay attention" is about as complex as this gets. The fact that we're susceptible to the specific timbre of their voices seems likely to be evolutionary coincidence.
Yes and, you missed the last crucial step
“Make noise = human pay attention” "Human feeds and protects me = more kittens that probably know to pay attention" ... "Profit"
It's likely not a coincidence but something they learnt a looong time ago living among humans.
Here's a study that goes into the frequency thing:
https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(09)01168-3
Did they model their meows, or did they have a trait that happened to work in a new environment and then pass it on?
From my understanding, wild cats only meow when little and domesticated cats keep this juvenile trait into adulthood
Yes, but the question is if they model their meows to sound like human infants. We know they changed their behavior to meow when wanting attention from us. But I'd be willing to bet they didn't model their meows to sound like that. They just happen to sound like that because they're small animals with high pitch voices.
There's a good chance that it's just a mammalian trait that predates modern humans or house cats. Pretty much all mammals require some extra protection and care when they are young and vulnerable, so it being common among other mammals isn't exactly surprising.
"They modelled their meows to sound like human infants" implies active intent, but (I'm sure you know) that's not how evolution actually works. If the theory is correct, their meows would naturally evolve to sound more like babies because those are the cats that we would be more likely to take care of, whereas cats with meows that sounded less like our babies would be less likely to be taken care of, and thus less likely to reproduce.
Or: people who didn't respond to these meows didn't keep their cats and rats ate all their grain so people more responsive to the meows reproduced more...
To my knowledge that's a lot of how domestication winds up being.
What I found interesting was a study when they tried to domesticate silver foxes for the fur industry (because basically they didn't take to being raised in fur farms well). So basically they were selectively bread for not being aggressive to humans.
Which worked, but the drawbacks were effectively... all of their childlike traits remained. IE their ears stayed floppy, and they stopped growing the silver coat that was the whole reason the fur industry wanted them.
Basically I think it could be said that effectively... most domestication traits are more or less, keeping childlike mentality for life in animals.