Kinda curious as to the point of drive encryption if you just want it to automatically unlock on boot.
Linux
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Linux is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution (or distro for short).
Distributions include the Linux kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name GNU/Linux to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy.
Rules
- Posts must be relevant to operating systems running the Linux kernel. GNU/Linux or otherwise.
- No misinformation
- No NSFW content
- No hate speech, bigotry, etc
Related Communities
Community icon by Alpár-Etele Méder, licensed under CC BY 3.0
It's disappointing to see so many commentors arguing against you wanting to do this. Windows has it through bitlocker which is secured via the TPM as you know. Yes it can be bypassed, but it's all about your threat level and effort into mitigating it.
I am currently using a TPM on my opensuse tumbleweed machine to auto unencrypt my drive during boot. What you want to do is possible, but not widely supported (yet). Unfortunately, the best I can do is point you to the section in the opensuse wiki that worked for me.
https://en.opensuse.org/SDB:Encrypted_root_file_system
If you scroll down on that page you'll see the section about TPM support. I don't know how well it will play with your OS. As always, back up all your files before messing with hard drive encryption. Best of luck!
Sums up about every thread asking how to do something on Linux, 30 different responses on how the OP is wrong and shouldn't do it that way.
To be fair there are probably many different ways to solve the problem. I'm somewhat experienced with Linux and I've attempted seeing up TPM LUKS decryption on boot. It's certainly not easy or at least wasn't when I tried. For non experienced people it's easier to just enter the password at boot and enable auto login. Then you get the security, software, ethics, or licensing debates that accompany most Linux discussions.
Windows is no baseline for security lol
OP, just change your encryption key to whatever you have your password as and set your login to auto login. This will give you the experience you desire as it'll decrypt the disk with your password and log you in automatically once it's decrypted, but if you lock the system (close the lid. Screen lock. Etc) you'll still get a login screen as normal. (Just keep in mind they're technically two separate passwords and will unfortunately need to be changed separately if you do change your password).
What I do for a little extra security is that my encryption password is just a longer variation of my normal password. So of I have an encrypted password sentence like "correct battery staple horse" my login password would just be "correct battery". It's a simple way to add a little extra and a good reminder everytime I turn on my computer that they are in fact two different passwords and protect me differently.
EDIT: Based on the responses I have to assume some of you guys live in windowless underground bunkers sealed off with concrete. Normal people don't need perfect encryption they just want to add an extra hurdle or two for the crackhead who steals the PC. I assumed Linux had a system similar to what Windows or MacOS has been doing for a decade but I am apparently wrong.
I am sorry you were treated like this and downvoted for just asking for help without being a jerk at all.
You ended up with full disk encryption. For most people, it's the simple option, everything is encrypted. That means the OS can't start without the key, because you're the only holder of the key. It's both dead simple, and pretty bulletproof since there's no way to access the system without the password. But as you said, not everyone wants that.
What you're asking for is an encrypted home directory. It's not that Linux can't do it, it's just not what you got. Depending on the use case you can either use TPM to unlock the root partition to boot, or not encrypt the system itself. Then when you log in, it decrypts a separate partition (or use ZFS native encryption, or use fscrypt if your filesystem supports it, or use an overlay filesystem like go-cryptfs).
So it's not that Linux doesn't support your use case but rather your distro doesn't offer it as an installation option. From there you either configure it yourself (ArchWiki is great regardless of distro), or seek out a distro that does.
Linux is not an operating system, it's just the kernel. What makes it an OS is what distros build on top of it. Linux alone is not that useful, hence the basis of the GNU+Linux memes: it's Linux, plus a lot of GNU tools to make it do useful things, plus a desktop environment and a whole bunch of other libraries and applications, plus the distro's touch tying it all together in a mostly cohesive experience.
I was kinda annoyed at double password login when I setup my system too. So what I did was just enable automatic login for my user since I’m the only one. I just treat my disk password as my login form so I just enter one password. I still have a user password for things like sudo and other permissions handling when I’m logged in but getting into a new session is automatic on startup so it doesn’t annoy me anymore. Would that work for you?
That's exactly what I do lol.
Assuming you want:
- Single password prompt instead of auto-decrypt with tpm
- User's files to be encrypted
There are several ways to achieve this:
-
autologin (recommended for single user system): / is encrypted using luks or zfs native encryption and user's home needs to be unencrypted. User's password may be same as encryption password for convenience, though they still are two passwords used for different purposes.
-
pam mount: / is unencrypted or auto-decrypted and user's home is encrypted independently from / using zfs,luks,fscrypt,etc. In this case, user's login password must be same as user's home encryption password. It's suitable for multi-user system. NOTE: It cannot be used with autologin since user's home needs to be decrypted to log in.
WARNING: For tpm usage, using secure boot is highly recommended to prevent unauthorized user from accessing key stored in tpm.
To prevent auto-decrypt with tpm, tpm-pin can be used (with autologin for requirement #1).
-
systemd-cryptenroll with/without tpm: As far as I know it can be only used to unlock disk encrypted with luks2. It can be used without tpm with pkcs11-token (e.g. YubiKey) or fido2-device. It also uses parameter encryption while key is unsealed, so safe from key sniffing via communication bus. This is easy if secure boot is enabled and luks2 is used for encryption.
-
clevis with tpm: It can be used in place of systemd-cryptenroll. May be used with zfs native encryption. Though I'm not sure if it uses parameter encryption (correct me).
-
unencrypted keyfile on usb: Not sure about zfs, but you can use keyfile on a usb drive to decrypt luks containers.
NOTE: I'm not a forensic/security expert. I listed a brief overview of methods I could think of to keep user's files encrypted while providing single password till login.
Auto decrypt with TPM sounds fine to me but I have no idea what TPM is as this is my first PC with it.
Thanks for the great response though I'll look into these
I have no idea what TPM is
Read Skull giver's reply or look it up.
Re-reading your post, I take you want to avoid typing long and tedious password? And that's why you want to auto-decrypt?
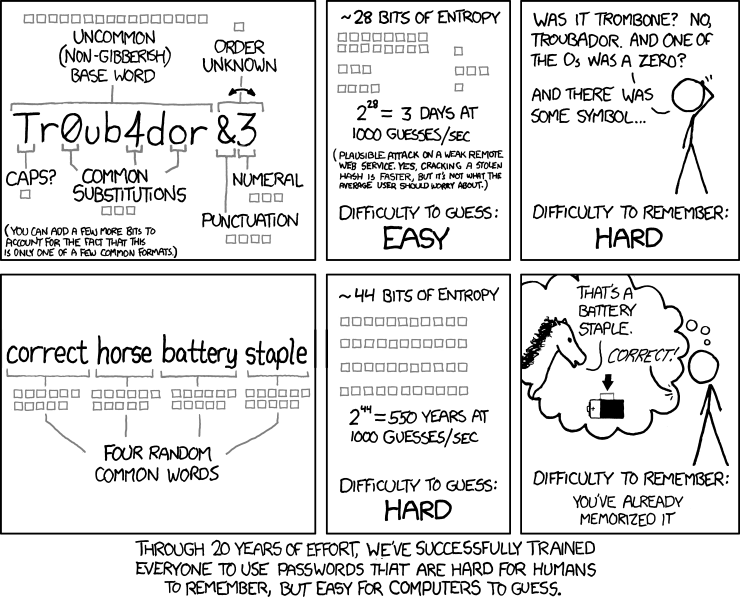
- (Recommended) You could use strong memorable passwords that are not difficult to type and enable autologin. Related xfcd comic:
- systemd-cryptenroll: For TPM usage, I highly recommend using secure boot. Though not sure if you can easily do that. A less secure alternative using systemd-cryptenroll would be use tpm2-pin and bind key to no pcrs (discouraged). But then you'll have to use luks2 for encryption.
Notice from
man systemd-cryptenrollregarding tpm2-pin:
Note that incorrect PIN entry when unlocking increments the TPM dictionary attack lockout mechanism, and may lock out users for a prolonged time, depending on its configuration. The lockout mechanism is a global property of the TPM, systemd-cryptenroll does not control or configure the lockout mechanism. You may use tpm2-tss tools to inspect or configure the dictionary attack lockout, with tpm2_getcap(1) and tpm2_dictionarylockout(1) commands, respectively Also tpm2-pin is not disk encryption password and short alphanumeric password needed so tpm decrypts the device; so encryption password should be secured in a safe place. Also check if your distro supports systemd-cryptenroll.
-
usb drive: read previous comment
-
clevis: It probably isn't as simple as systemd-cryptenroll but I guess you can use zfs and combine that with tpm2-pin if not using secure boot (discouraged).
You'll have to make a compromise somewhere between security and convenience. Even if you use pam mount, you'll have to enter the password, biometrics won't do.
Edit: remove unnecessary user tag and add img uri
Afaik you can't. Disk encryption requires entering the password every time and it asks for it BEFORE the OS is started so you can't use biometric login either
Others have given you ways of doing this, with TPM or hacking away by using the same password and auto-login. Many have told you you shouldn't, but I think no one explained why.
When the bootloader chooses the OS that OS might be on an encrypted or an unencrypted disk. If the OS is on an unencrypted disk it can be easily hacked and then all bets are off. So the only safe option is if the OS is on an encrypted disk, however to do that you need to decrypt the disk to access it. Now there are two options, either you need to provide a key for decryption (it does not need to be a password, it can be a thumb drive or fingerprint) or it happens automatically. If it happens automatically it's the same as not having encryption.
Enter TPM, which is trying to safely automatically decrypt the disk by using hardware validation. However here's the problem, the only reason you need disk encryption is to prevent against your hardware being stolen. If your hardware was stolen and you don't have disk encryption people can simply read the data. If you have disk encryption they need to decrypt the disk first. However when you use TPM or anything similar the disk gets decrypted automatically, meaning that it's almost the same as not having encryption at all.
If a hacker got a hold of your unencrypted disk they can open it on a second OS and extract the data. If they got a hold of a fully encrypted disk they are more or less screwed. But if your computer unencrypted the disk on boot all they have to do now is access the disk from your OS. There are several ways of bypassing a login, brute force it, or create new users. Not to mention possible security issues that might give the attacker access to your entire system, which is already unencrypted. Yes, having some form of encryption, even if it unencrypts automatically is better than no encryption at all, but not by much. I would argue that if you care about the data not being accessed you shouldn't have it decrypt automatically, and if you don't mind it decrypting automatically then encryption might be overkill for you.
Yes there is TPM for full disk encryption.
https://gist.github.com/orhun/02102b3af3acfdaf9a5a2164bea7c3d6#using-tpm-20
Do I had problem making swap partition work. As lockdown mode is triggered.
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/kernel_lockdown.7.html
I current only encrypted home.
Instead of encrypting the entire drive, encrypt the home folder. That way it’s unlocked when you sign in.
If you want some more convenience but don't want to give up security, you can use hardware tokens like Nitrokey with GPG.
The process would be generate a random file using dd and /dev/urandom. Set this as the key for FDE. Encrypt it using your GPG and store it on /boot. Have a helper script to ask you plugin your Nitrokey and (optional) pin to decrypt the keyfile to have root decrypted. I had read this on some blog for dm-crypt so you will need to research and adopt to your setup.
If it’s LUKS encryption, yeah, you can unlock it with the TPM. I forget how. Basically you add another key to LUKS that comes from the TPM. There are guides online.
The common way to do it with LUKS2 and TPM as detailed on the Arch wiki. Not sure if that'll apply at all to ZFS and Zorin though
It is less secure though. What I do is set my computer to log in on start and I set up fingerprint auth. So I only need to login once on startup with the drive decryption.
Here's a reddit post on using clevis, TPM, and ZFS to decrypt.
You should also know that if you're mobo dies so does your data.
If you want to do away with any protection you have with opting in to a security measure, like typing in a password, why don't you just reinstall and not select the encryption option?
Not requiring a password, or automatically entering a password to decrypt the filesystem, is essentially the same as not having encryption.
Decide which you want: Security or convenience. You cannot have both.
This reply isn't going to be helpful to OP, but thought I might add context for others passing by.
I'm using Arch Linux with LUKS encryption and gdm. As long as my user's password is the same as the LUKS password, I only ever type my password in once.
Just saying that a MacOS-like convenience is definitely possible on Linux.
You dont want to do that.
What's the point of encrypting something without a good passphrase? It defeats the whole purpose.
Thats how encryption works. Encryption with TPM protects against removing the drive and reading somewhere else, so I suppose it makes sense for most people.
Linux Distros have this option, Ubuntu has it now I think, but on the others its often manual setup.
Just search for "cryptsetup change to tpm"