Space
9192 readers
70 users here now
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
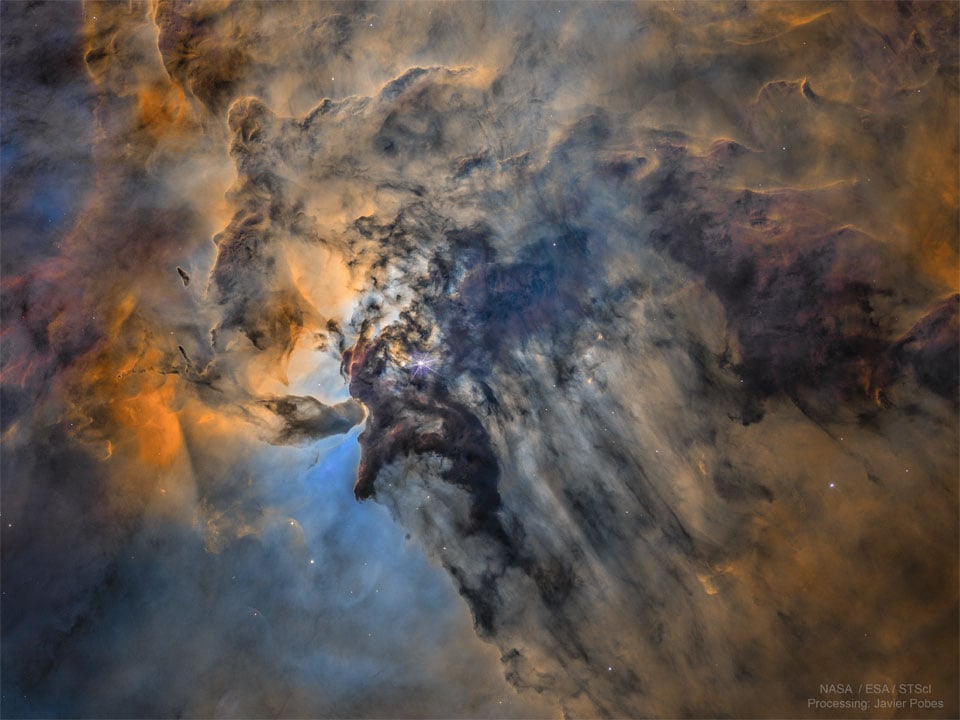 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
201
202
203
36
China's 30-satellite information superhighway to connect Earth, moon
(interestingengineering.com)
204
127
Astrophotographer takes stunning photographs of the sun in incredible detail from his backyard in Arizona
(www.digitalcameraworld.com)
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
73
Astronauts confident Boeing space capsule can safely return them to Earth, despite failures
(finance.yahoo.com)
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
