Space
9422 readers
360 users here now
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
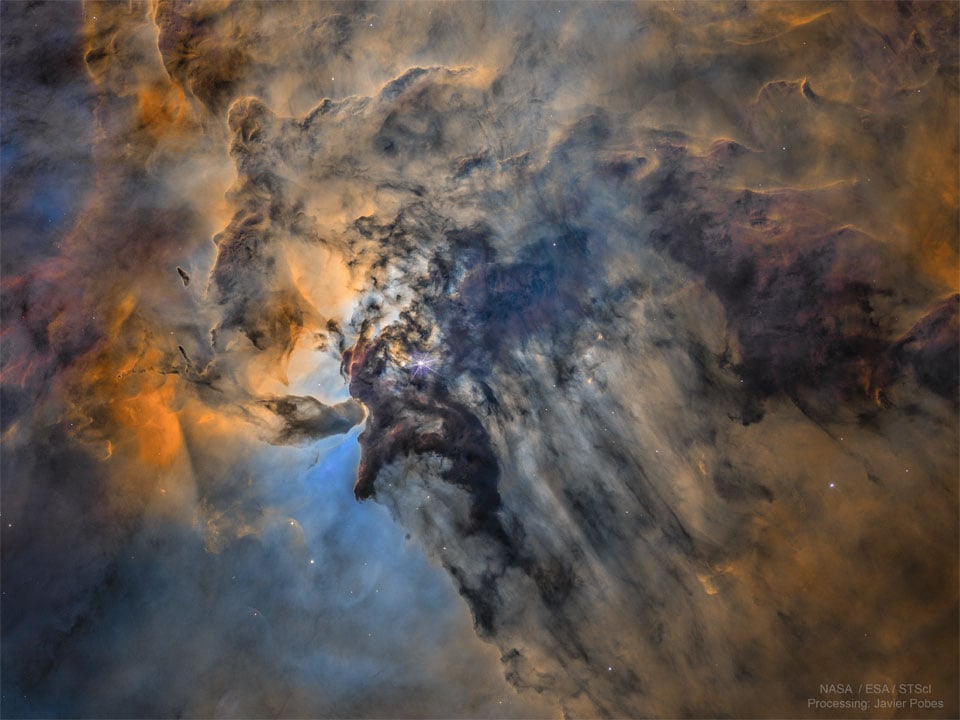 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
802
465
803
804
805
18
Astronomers puzzled by ‘weird’ planet whose atmosphere is being ripped off by its sun
(www.independent.co.uk)
806
807
808
809
810
811
812
68
813
124
A new, Jupiter-size planet is on the verge of being born, and astronomers have incredible images of it
(www.livescience.com)
814
815
816
817
818
819
820
821
822
823
824
825

