[🌽].pop() == 🍿
Programmer Humor
Post funny things about programming here! (Or just rant about your favourite programming language.)
Rules:
- Posts must be relevant to programming, programmers, or computer science.
- No NSFW content.
- Jokes must be in good taste. No hate speech, bigotry, etc.
"🚴".push() = "🚲🤸""☹️".reverse() == "☹️"You're no fun
Look closer at the beauty mark, I flipped the emoji
wasn't it
🙁
.
r
e
v
e
r
s
e
()
"
🙂
"
.
r
e
v
e
r
s
e
(
)
=
"
🙃
"
Then “b” backwards would have to be “d”
"E".reverse() == "∃"
Be the operator overload you wish to see in the world
":-)".reverse() == ")-:"
Close enough
Also, it should turn an error into an empty but successful call. /s
Calling reverse() on a function should return its inverse
isprime.reverse(True)
// outputs 19 billion prime numbers. Checkmate, atheists.It's a just a joke, but I feel like that actually says something pretty profound about duck typing, and how computable it actually is.
"🐈".concat() = "😼"but
"🙂".reverse() == "🙃"
Best I can do is
"\ude41🙂".split("").reverse().join("")
returns "\ude42🙁"
JavaScript taking notes
You could implement that on a chat, but I wouldn't do that on a string
Where's your sense of adventure?!
Today I found out that this is valid JS:
const someString = "test string";
console.log(someString.toString());
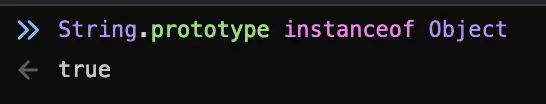
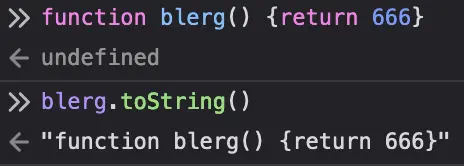
Everything that's an Object is going to either inherit Object.prototype.toString() (mdn) or provide its own implementation. Like I said in another comment, even functions have a toString() because they're also objects.
A String is an Object, so it's going to have a toString() method. It doesn't inherit Object's implementation, but provides one that's sort of a no-op / identity function but not quite.
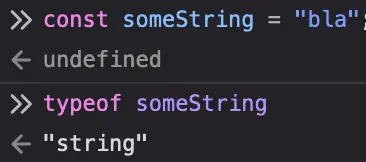
So, the thing is that when you say const someString = "test string", you're not actually creating a new String object instance and assigning it to someString, you're creating a string (lowercase s!) primitive and assigning it to someString:
Compare this with creating a new String("bla"):
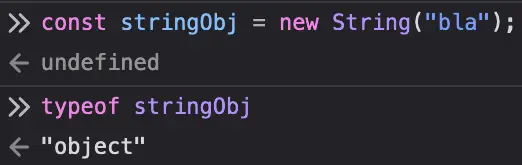
In Javascript, primitives don't actually have any properties or methods, so when you call someString.toString() (or call any other method or access any property on someString), what happens is that someString is coerced into a String instance, and then toString() is called on that. Essentially it's like going new String(someString).toString().
Now, what String.prototype.toString() (mdn) does is it returns the underlying string primitive and not the String instance itself:
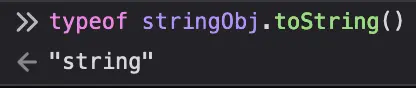
Why? Fuckin beats me, I honestly can't remember what the point of returning the primitive instead of the String instance is because I haven't been elbow-deep in Javascript in years, but regardless this is what String's toString() does. Probably has something to do with coercion logic.