A new report details an ongoing shortage of laxatives, purportedly fueled by an aging population and gut health TikTok influencers.
It might be time for Americans to start eating more fiber. The U.S. is experiencing a shortage of laxative products, according to a report this week from the Wall Street Journal. One alleged reason for the short supply is extra demand from younger people—an interest apparently fueled by TikTok influencers touting the supposed benefits of laxatives for good gut health.
The shortage concerns polyethylene glycol 3350, the active ingredient in many laxative brands, such as MiraLAX. According to a report from the analytics company Pattern, cited by the Wall Street Journal, product searches for laxatives have more than tripled over the past year on Amazon, while fiber product companies have reported an significant increase in sales as of late. The outlet also interviewed both gastroenterologists and suppliers about the drug’s declining availability, who offered several long- and short-term explanations for the increased demand.
The average American is getting older, for instance, and older people are more likely to regularly suffer from gastrointestinal conditions like constipation. The pandemic also changed many people’s dietary habits for the worse, leading to an increase in eating unhealthy snacks and other foods more likely to cause constipation. And at least part of the demand might stem from TikTok fans tuning into #GutTok, filled with people offering folk remedies for any number of gastrointestinal health issues.
GutTok has been a trending topic on the social media platform for quite some time, with influencers claiming to know the best way to reduce bloating, improve mood, and even clear acne by improving your gut health. While some of the provided suggestions for a better gut are likely to be harmless at worst, such as drinking more water, other ideas can be actively harmful, and that can include an overreliance on laxatives.
Chronic laxative use can worsen a person’s constipation further, to the point where they need higher and higher doses to pass their stool. They can also cause long-term damage to the intestines and raise the risk of rectal prolapse, a condition where the rectum slips out of the anus. And acute side effects like dehydration or stomach cramps aren’t exactly a picnic.
Though the occasional laxative is fine, people’s gut health would be better served by sustained positive changes in their lifestyle and diet, such as eating more fruits and vegetables as well as getting plenty of exercise. Whether these changes are possible on a widescale level in the U.S. anytime soon is another question.
“It’s crazy to think that our collective bowel dysfunction problems have gotten so bad that we’re literally running out of stool softeners,” George Pavlou, President of the Gastroenterology Associates of New Jersey, told the WSJ.
Some medications can make you constipated. Opioids, for instance.
How many people do you think are on opioids at any given time? Enough to cause a laxative shortage?
Well we do have a whole opioid addiction crisis going on.
We have an even bigger obesity/terrible diet crisis going on too though.
Three million US citizens and 16 million individuals worldwide have had or currently suffer from opioid use disorder (OUD).
-StatPearls Publishing via The National Library of Medicine
You know what, this map is a much better source for this (the CDC).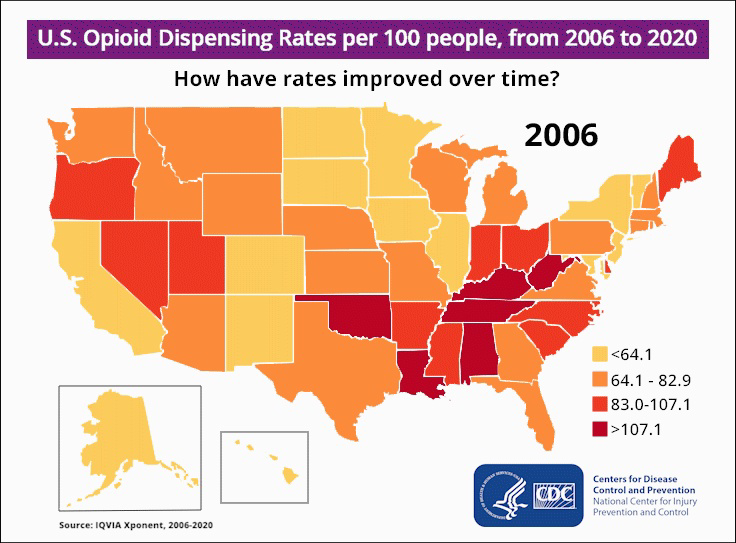 https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/rxrate-maps/index.html#:~:text=The%20overall%20national%20opioid%20dispensing%20rate%20declined%20from%202012%20to,than%20142%20million%20opioid%20prescriptions).
https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/rxrate-maps/index.html#:~:text=The%20overall%20national%20opioid%20dispensing%20rate%20declined%20from%202012%20to,than%20142%20million%20opioid%20prescriptions).