Technology
This is the official technology community of Lemmy.ml for all news related to creation and use of technology, and to facilitate civil, meaningful discussion around it.
Ask in DM before posting product reviews or ads. All such posts otherwise are subject to removal.
Rules:
1: All Lemmy rules apply
2: Do not post low effort posts
3: NEVER post naziped*gore stuff
4: Always post article URLs or their archived version URLs as sources, NOT screenshots. Help the blind users.
5: personal rants of Big Tech CEOs like Elon Musk are unwelcome (does not include posts about their companies affecting wide range of people)
6: no advertisement posts unless verified as legitimate and non-exploitative/non-consumerist
7: crypto related posts, unless essential, are disallowed
view the rest of the comments
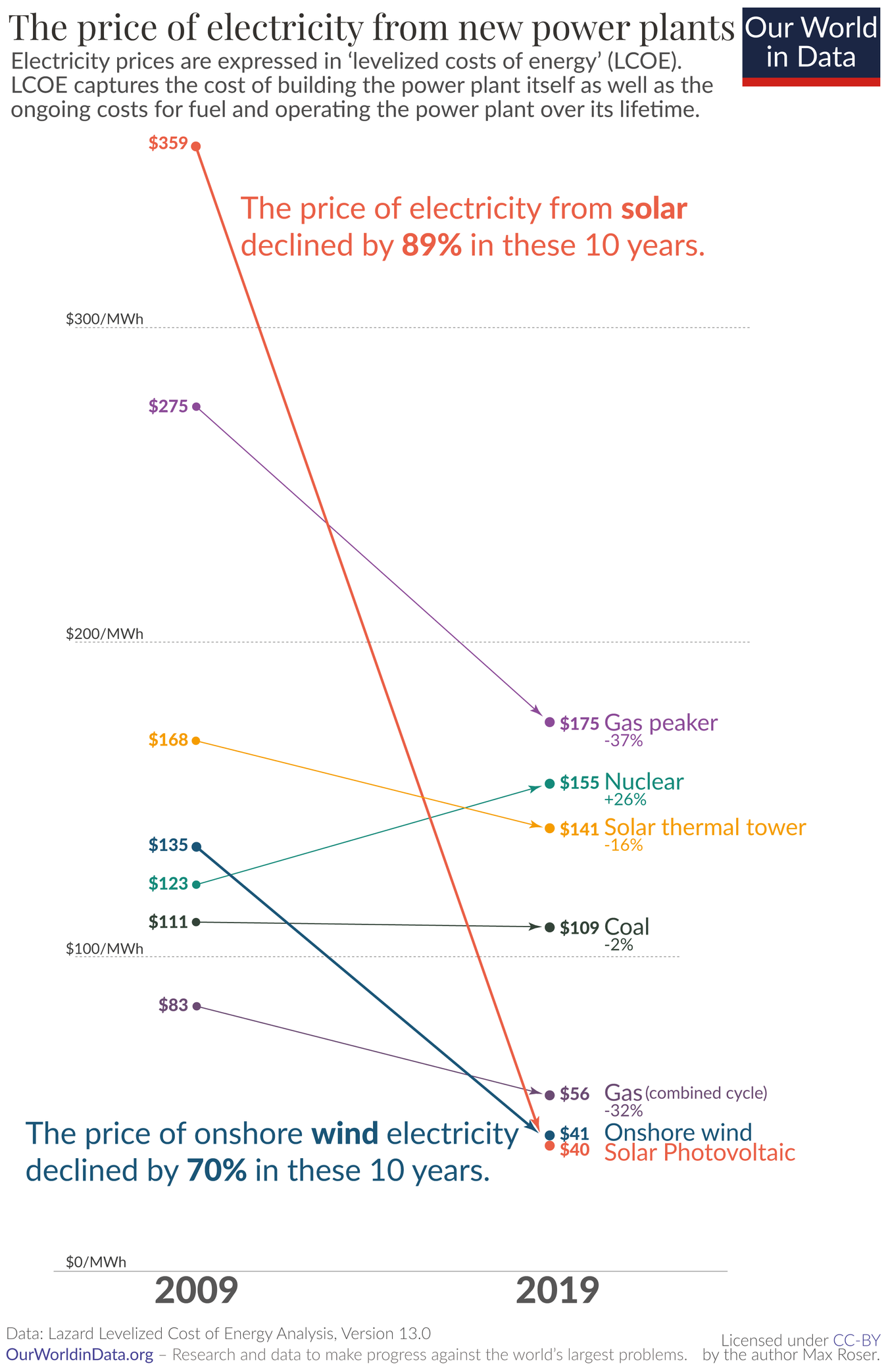
Cool…but where’s offshore wind?
I'm not quite sure, why it was left out of that graph, maybe they didn't have matching data, but it is shown here (from the same source article):
Clearly nuclear is the future!
You do realise solar and wind gets pricier and pricier to integrate as the level of steerable capacity decreases?
What you are looking at here is “cost to install ‘rated capacity * load factor’”. A big part of the reason renewables are still cheaper is that we have a lot of backup steerable capacity, mainly in the form of gas plants in the west and coal plants everywhere else.
Renewables dump electricity onto the grid and then say “here, buy this!”. And the only reason the grid can respond and say “sure” is that it can tell the steerable gas and coal plants “turn off for a bit, these other plants are dumping a crap tonne of capacity onto the grid”.
Given the insane challenge in building enough storage and/or enough transmission capacity, you are going to need some steerable capacity beyond 70-80% renewable to continue to have cheap integration of intermittent renewables. Do you want that to be based on fossil fuel?
If we wanted to treat renewable capacity in the same way as we have treated other generators, we should say “I want steerable capacity between 0-1200 MW” from this field of wind turbines!”. That would force the currently externalised cost of guaranteeing generation onto the builders of renewables.
Right now, a lot of the real cost is hidden elsewhere in the grid - so it’s no wonder it looks so cheap.
Please don’t misread my comment as being against renewables, which we need a lot more of. I’m against crappy accounting.
However, your point also goes ageinst nuclear as this technology is not really steerable either. It produces a base supply. The lack of quick control of nuclear plant output even led to highways beeing lit in the night in Belgium (way back) to burn off the over supply.
The only technologies that can be quickly adjusted up and down are, to my knowledge, gas, hydro an battery storage. In a strictly renewable scenario (0 fossil, 0 nuclear fisson) it is imperative to have a lot of controllable reserves. Currently the plan is to use a mix of (pump) hydro, h2 and biomass powered gas plants and batteries in all shapes and forms (li-Ion, reflow, heat...) to be able to compensate peaks. This all is way more costly than just using wind and solar and hope supply will always be higher than demand.
For those interested I always recommend the yt channel "just have a think". It has really awesome content about green technologies and the current state of affairs concerning the long and hard journey to 0 carbon.
That is honestly an urban myth that nuclear isn’t steerable. It’s not steerable in the second, but it is extremely steerable in the hour or the day, which is more than plenty given that renewables output change by the hour or day, rather than the second.
Yes it’s not frequency management - for that we have pumped storage and batteries. But it sure as shit is steerable enough for matching up with renewables. The wind doesn’t goes from Beaufort 6 to Beaufort 1 within a second.
This is a very interesting rabit hole you sent me into. Thanks for that!
Btw. I don't get why you're beeing downvoted. This is a civilised discussion and your comments are fair and well presented!
I started searching a bit about steering nuclear.
So as usual it doesn't seem to be quite so simple. I found a paper from 2017 (in German https://publikationen.bibliothek.kit.edu/1000102277/121070976 ). interesting parts translated through deepl/chatGPT:
"The operating manuals of the NPPs show that they [nuclear power plants] exhibit considerable flexibility:
In the range close to full load (above 80/90% of the nominal Power), the output can be increased or decreased by up to 10% of the nominal output per minute. In the upper load range (above 50/60 % PNenn), the power plants can be regulated at 3.8-5.2 %/min (for some reactor types, this is reduced to around 1 %/min if individual fuel rods are defective).
For comparison: In lignite-fired power plants, this value is around 3 %/min, 4 %/min for hard coal-fired power plants and 6 %/min for natural gas steam or combined power plants 6 %/min. Only gas turbines, at 12 %/min, are significantly faster.
The lower load range (between 20 and 60%) is also possible, but in discussions with power plant operators it became clear that this has not yet been used in regular operation (apart from start-up and shutdown operations) and is not used in regular operation."
Also it seems that changing output puts stress on the whole systen. As well cited from the paper:
"Another factor is the number of cycles that the plants can undergo. Each load cycle stresses the material and, with frequent repetition, leads to signs of material fatigue. Nuclear power plants were designed for a specific maximum number of cycles during their construction. In the upper load range – for example, a reduction in power from 100% rated power to 80% and back (100-80-100) – coolant temperature and pressure hardly change. Therefore, the power plants are designed for up to 100,000 cycles of such nature. However, in the lower load range, the alternating stress on the components increases, and the maximum cycle count decreases significantly. The cycle 100-40-100, for instance, is allowed only 12,000 repetitions. For the cycle rated load-zero load-hot-rated load (100-0-100), a maximum of 400 cycles is specified. Assuming a plant lifespan of 40 years, this would correspond to 10 of these events per year."
So there seems to be considerable flexibility but you don't want to shut it off completely or run below say 50% of nominal power. Also start-up times from 0 seem to be very long (1-2 days). This might not be the perfect match for running together with renewables, but there are definitively possibilities. Even when it's windy and the sun shines, renewables would need to be shut down and the more expensive nuclear plant would run and burn fuel.
Therefore, my opinion still stands: the ultimate goal should still be 0 burning stuff, 0 nuclear.
Hey, likewise, thanks for a sensible debate.
I definitely think 0 nuclear is possible, just a lot expensive than “mostly renewable with some nuclear.”
I’ve commented extensively on this before here on Lemmy, let me copy pasta here:
Here’s a couple of good papers and articles on the topic:
A systematic review of the costs and impacts of integrating variable renewables into power grids - a large meta-study from Nature Energy showing that the externalised additional cost of integrating 1 MW of renewable production hits £40/MWh between 75% to 85% renewable penetration. Beyond that no studies have been done, but already at this level, renewable would be more expensive than nuclear (at auctioned build-prices today).
Real-World Challenges with a Rapid Transition to 100% Renewable Power Systems - finds that even if you set the Value of Lost Load to £40,000/MWh in a 100% renewable grid, you’ll still get power outages after 2030. It’s not equivalent to externalised cost of renewable integration, but is a heavy indicator that without forcing massive fines on renewable providers, the reserve capacity won’t be provided (it’ll be cheaper for them to just pay the fine). The study finds that a fine of £4 million (!) per required-but-not-fulfilled MWh is needed to encourage providers build the reserve capacity (through distribution, storage etc.).
How much can nuclear power reduce climate mitigation cost? - shows that nuclear will lower the cost of getting to zero carbon electricity product by 40%+, compared to refusing to use nuclear energy production.
Burden of proof: A comprehensive review of the feasibility of 100% renewable-electricity systems - shows some of the challenges of the assumptions that people make in thinking renewables will get us all the way there.
Projected Costs of Generating Electricity - shows that, all costs considered, nuclear remains an extremely cheap way to create energy, even up against renewables.
Local Complementarity of Wind and Solar Energy Resources over Europe: An Assessment Study from a Meteorological Perspective - shows that at least in Europe, wind and sun don’t anti-correlate (in other words, we’re not going to get energy from the sun on non-windy days and energy from the wind on cloudy days. Also shows there are many periods (days long) in Europe where we have don’t get neither sun nor wind. So storage will have to last us days across Europe.
Many of these articles refer to many other articles you may find interesting.
Overall, my point is that it does us (collective “us”, not just “you and me”) no good to argue that “it’ll be alright if we just commit to renewables”. One has to argue against these peer reviewed studies, done by experts in the field, many collecting and meta-reviewing many other studies, to argue that “renewables will be enough”.
And these are not “cooky studies” in “cooky journals”. Nature, Cell, Joule are some of the most respected journals, with the highest impact ratings and the authors & their reviewers have studied these topics for years.
I’m all for more renewables! But it won’t be enough!
also since fuel costs aren't really a problem for nuclear power, you can just throw away excess generation. not the best idea but perfectly possible in a pinch
Wind and solar complement each other. The sun often shines when the wind isn't blowing. We have plenty of historical weather data on how long the lulls where neither would work for a given region. That tells you how much storage you need to fill the gap. Pad that out, and you're good.
Nuclear does nothing to help this calculation. It's just expensive.
Not only that, but we don't have to do this all at once. The math often works out that getting to 95% renewable is far easier than shooting for 100%, with existing fossil fuel plants making up the remainder. This is fully achievable by 2030, by which point we want to drastically reduce emissions. Then we can worry about the last 5%.
There is no such plan for nuclear. If you had all the permits signed off and dirt being shoveled right now, then you would not have a single MW of new nuclear feeding the grid by 2030. They take too long to build. Budget and schedule overruns are the norm, and it's a wonder that anyone is investing money into them at this point.
In fact, they aren't. The US federal government has shown a willingness to sign permits for new nuclear plants. Nobody is buying, and there's no mystery as to why.
The reason nuclear plants take so long to build is because there is so much ignorant opposition to them. The same roadblocks that caused our global housing crisis get in the way of building clean nuclear energy.
Even if that's true, what's your plan to fix it? You cannot ignore NIMBYs. You need a plan.
the plan is to neuter the NIMBYs power. same problem as housing. you have to defeat the NIMBYs because they're the problem and getting rid of the problem is the solution
We just have to build a transatlantic power line - It's always sunny somewhere in the world /s
yeah, do a nuclear backup for renewables. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integral_Molten_Salt_Reactor this reactor outputs solar salt, which can store energy efficiently for hours and allow load following
dat place called Scotland?
No, silly. That’s onshore. Scotland, see? Land means, y’know, on shore? I want to know about the windmills in the ocean.
(Do I have to put this here? /s)
Kind sir, with the current tendencies in overall temperatures that excite changes on the far north and south, you simply have to be patient till onshore become offshore just as you desire.