this post was submitted on 25 Oct 2023
744 points (95.7% liked)
privacy
3090 readers
1 users here now
Big tech and governments are monitoring and recording your eating activities. c/Privacy provides tips and tricks to protect your privacy against global surveillance.
Partners:
- community.nicfab.it/c/privacy
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
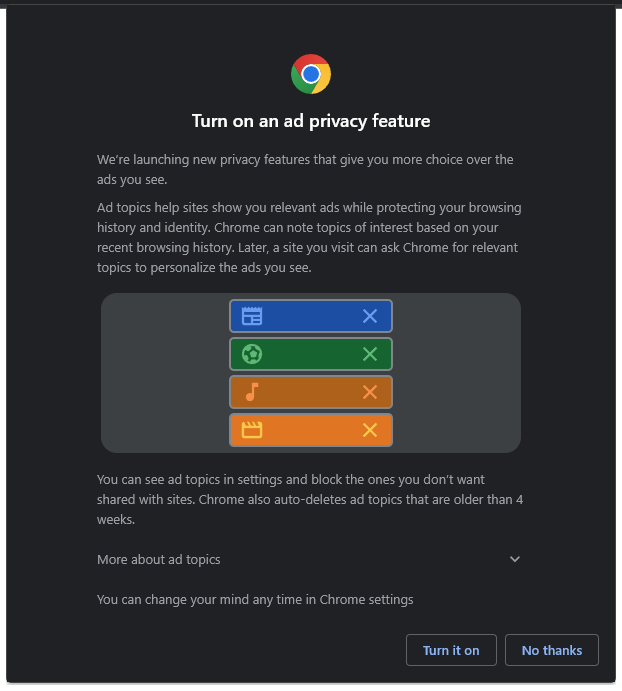
There is a lot of misinformation being shared in this thread.
A good excerpt from Steve Gibson covering Topics on SecurityNow #935
...
...
SecurityNow #935 transcript
Max that's a wonderful comment, but could you just tell me what to do, I ain't reading all that.
You should really practice reading more if something that long is difficult for you.
Reading is a crucial life skill that everyone should practice daily.
TL;DR: If you want to use Chrome then don't be worried about Topics. It's better privacy than third party cookies and other tracking methods.
Stop using Chrome either way. Topics are still tracking, just a different kind.
Right? "Here is a quick excerpt". Then proceeds to post a whole article.
Within the context of the subject matter, that was a quick excerpt. And, in fact, the transcript from which that excerpt was extracted can probably be considered a relatively quick excerpt from the entire system.
Sometimes it is just not possible to simplify further or be more concise without just saying "trust me, it's better than what we had up to now." That is especially true when we have all learned, I hope, that "trust me, I saw it on the internet" is a really lousy way to make decisions.
Damn bro, my bad. I must have been cranky when I left that comment. Totally understood!
No problem! If that's as nasty as we ever get, then I'd say we're doing pretty damn good!
tl;dr There are valid reasons to not use Chrome, and to be suspicious of Google. This, specifically, is not one of them and the fear is mostly overblown by people who have done zero research.