this post was submitted on 30 Oct 2024
384 points (97.3% liked)
Science Memes
13138 readers
2055 users here now
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
This is a science community. We use the Dawkins definition of meme.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !reptiles and [email protected]
Physical Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !self [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Memes
Miscellaneous
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
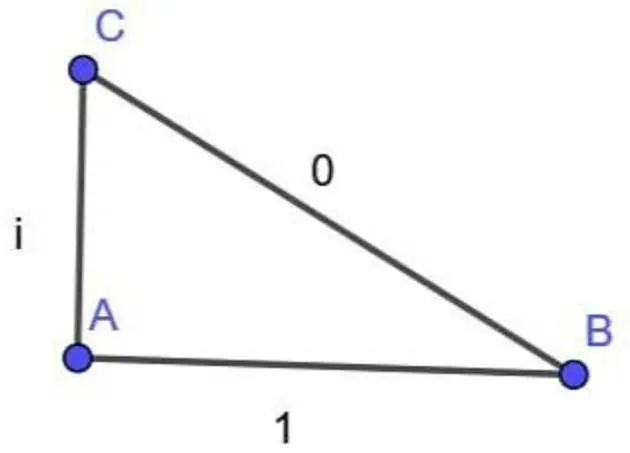
The reason it doesn't work is that 1 is a scalar while i is a vector (with magnitude 1). The Pythagoras theorem works with scalars, not vectors, so you'd get 1^2 +1^2 = 2.
Far as I understand it (which is not very far), i is a scalar even if you take it to be the complex number 0 + i. Just by itself i is the imaginary unit that's defined as i = sqrt(-1) (edit: or, well, the solution to x² + 1 = 0, but same difference), and nothing in that definition says it's a vector quantity.
Even though complex numbers do extend real numbers into a 2D plane doesn't mean they're automatically vectors, and – again, as far as I've understood things – they're still treated as single entities, ie. scalars. i by itself isn't a complex number I think, though.
The joke is that i² = -1 by definition, so i² + 1² = 0²
Edit: eg. nothing on the imaginary number wiki page implies that the imaginary unit is not a scalar value
whether or not i is a scalar depends entirely on the context.
every vector space has an associated field of coefficients. in practice, this field is typically the real numbers. but you can have lots of other kinds of vector spaces as well, and they can be useful for certain things.
anyways, if you have a vector space over the complex numbers, then i is a scalar, because it is a complex number. if you have a vector space over the real numbers, then i is not a scalar, because it’s not a real number.
its worth mentioning that you can view the complex numbers as a vector space over itself. this is just a fancy way of saying that you can add complex numbers together, and you can multiply a complex number by a complex number. (one of those numbers is playing the role of scalar, and the other is playing the role of vector.) but you can also view the complex numbers as a vector space over the real numbers. and this is just a fancy way of saying that you can add complex numbers, and you can multiply a complex number by a real number.
Right, sort of my vague understanding as well although it's been 15 years since my university math courses. My point was more that "1 is a scalar while i is a vector" just didn't seem correct to me, at least on a general level
ah true. i missed the context of the original comment since it got deleted, but you're completely right that the “1 is a scalar while i is a vector” statement is not entirely accurate.
I am sorry, but.. to be pedantic, pythagorean theorem works on real-valued length. Complex numbers can be scalars, but one does not use it for length for some reason I forgor.