this post was submitted on 16 Jul 2024
42 points (86.2% liked)
Asklemmy
45214 readers
1237 users here now
A loosely moderated place to ask open-ended questions
If your post meets the following criteria, it's welcome here!
- Open-ended question
- Not offensive: at this point, we do not have the bandwidth to moderate overtly political discussions. Assume best intent and be excellent to each other.
- Not regarding using or support for Lemmy: context, see the list of support communities and tools for finding communities below
- Not ad nauseam inducing: please make sure it is a question that would be new to most members
- An actual topic of discussion
Looking for support?
Looking for a community?
- Lemmyverse: community search
- sub.rehab: maps old subreddits to fediverse options, marks official as such
- [email protected]: a community for finding communities
~Icon~ ~by~ ~@Double_[email protected]~
founded 5 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
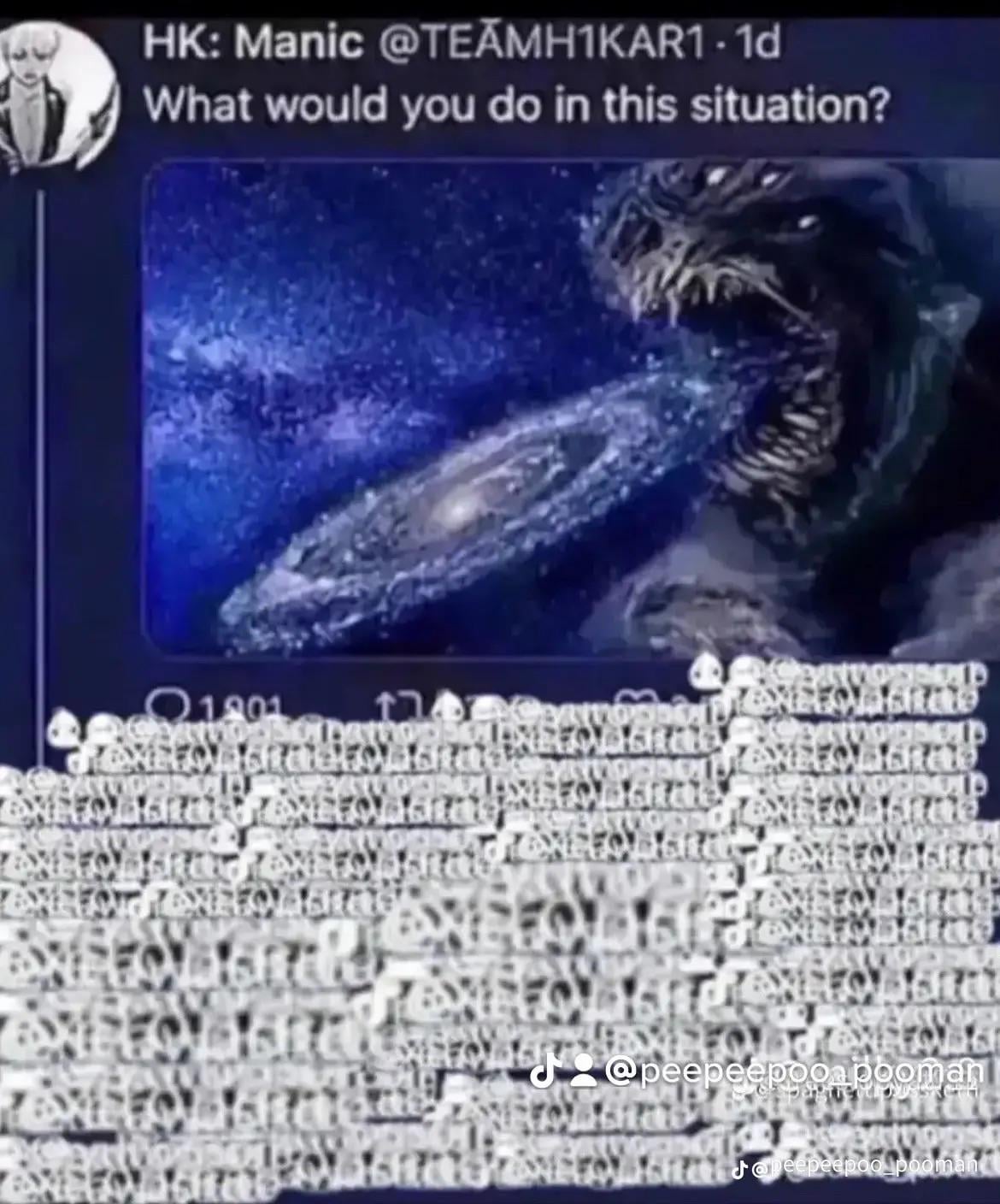
The speed of sound is the velocity a force can propagate in a medium, so yes even assuming such a mega structure is theoretically possible (it's not) it would close its mouth at the speed of sound.
If you want a galaxy-doom monster, either pick a super massive black hole, a super massime white hole, a super massive black hole coming out of a bigger white hole, or a super massive quasar pulsating high energy X-ray bursts with enough power to kill all life of an entire galaxy
That's not entirely accurate, the force it applies to close it's mouth would probably travel at or close to the speed of sound along its jaw, but it could reach the speed of light by applying that force if you ignore a number of problems. One of which is that it will turn into a black hole at that scale, it's much too dense.
On your second point, it's hard to make any of those into galaxy killers. Supermassive black holes exist at the centre of virtually every galaxy and don't do a ton, and even quasars only have limited killing range as there are limits to how collimated a beam of radiation can be. White holes are more complicated and I don't have enough space in a single comment to go into the nuances, but they're about as harmless as black holes really.
The only thing I can think of that would destroy all life in a galaxy would also destroy the universe, and that's to trigger a false vacuum decay, but that might not be possible anyway.