this post was submitted on 01 Jul 2024
25 points (90.3% liked)
Linux
49838 readers
556 users here now
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Linux is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution (or distro for short).
Distributions include the Linux kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name GNU/Linux to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy.
Rules
- Posts must be relevant to operating systems running the Linux kernel. GNU/Linux or otherwise.
- No misinformation
- No NSFW content
- No hate speech, bigotry, etc
Related Communities
Community icon by Alpár-Etele Méder, licensed under CC BY 3.0
founded 5 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
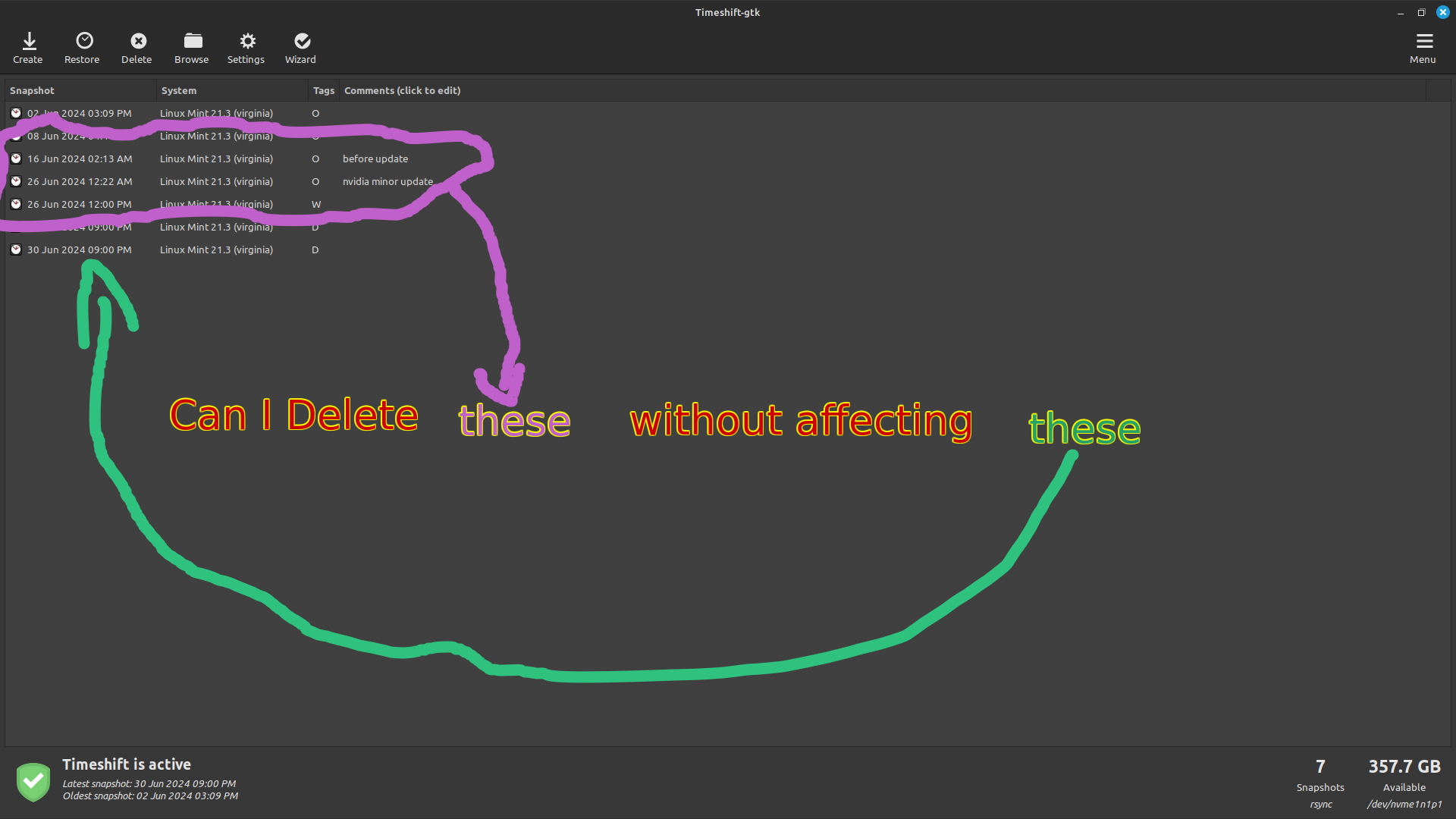
Because I still Don't know the difference between hardlinks and softlinks and symlinks 😅
Files on a hard drive aren't directly files. Folders, for example, are just metadata things which contain pointers to things like the previous directory and files within it (along with names) AND other metadata like owner, group, and permissions. Files have a similar metadata thing (they're called inodes) which things like owner, permissions, and a block manifest (where the data is stored) and critically: a count of how many things point to it.
This count is needed because of hard links. A hard link is two folders pointing to one of these file metadata blocks as different files. The count is used to ensure that a file that is still in use isn't deleted. This also means a hardlinked file must share at least some permissions. Most systems are also set up to only cache one copy of the file in RAM if such a situation were to come up.
So what I assume time shift does (can't use it because it has an aneurism when it sees a RAID drive for some fucking reason) is store independent "copies" of files per each backup, where only changed files are stored and the rest are hard linked. There is still storage used for the new folders but its on the scale of hundreds of KiloBytes. The software can purge one of the backups safely without affecting another, including the first backup.
A soft link is just a file that contains a file path. Like a shortcut.
Thank You. Still got to learn a lot.
If you look at the output of ls -l , you'll see a number on the left which tells you how the pointer counter. Folders are usually rather high, as both the parent folder, and any child folders point to it.
For files it counts the number of hardlinks.