Planning with Popsicles - A Clipper Celebration! - Curiosity Rover Blog for Sols 4334-4335. Earth planning date: Monday October 14, 2024
Today was an unusually exciting day during tactical planning on the Curiosity mission because it intersected with a momentous event in space exploration: the launch of Europa Clipper from Kennedy Space Center. Even though the launch window occurred right in the middle of our morning planning meetings, at 9:06 a.m. PDT to be specific, today’s Tactical Uplink Lead and Science Operations Working Group Chair agreed it would be OK for the entire tactical team to take a 15-minute pause to turn on NASA TV and watch the launch together. Down the hall the Perseverance rover tactical team had decided the same, and for a few moments, the two teams paused their planning and watched together in anticipation as the countdown ticked down to T-0. Many of my close friends and co-workers had worked for years — some for decades — to make this mission a reality, and it was amazing to watch the enormous rocket carrying the Clipper spacecraft leap off the pad knowing how hard it was to get to this point. I cannot wait for the mission’s discoveries once it reaches Jupiter’s watery moon Europa!
In true JPL tradition, we of course had to commemorate the event with some sweet frozen treats on-lab. Back when Curiosity landed, we had a full fridge of ice cream that was kept stocked for the first 90 sols of the mission. (Eating ice cream cones at 2 in the morning is a core memory of mine from those early days in our mission.) Today, in a clever nod to Europa’s icy surface, we celebrated with some even icier sweets: fruit and coffee popsicles to anyone on-lab. I chose coffee of course; the caffeine was great to help me get through a busy day of planning for Curiosity!
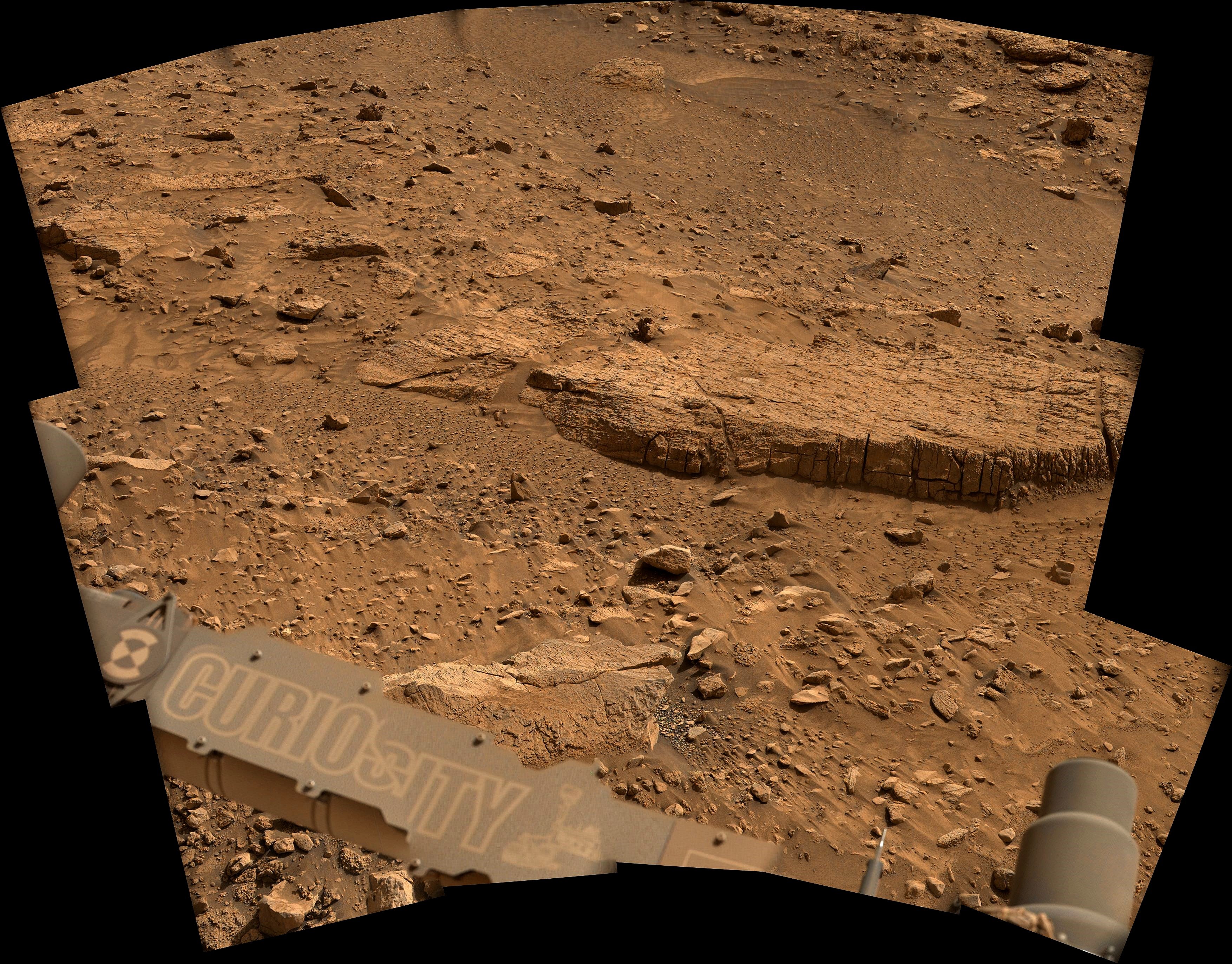
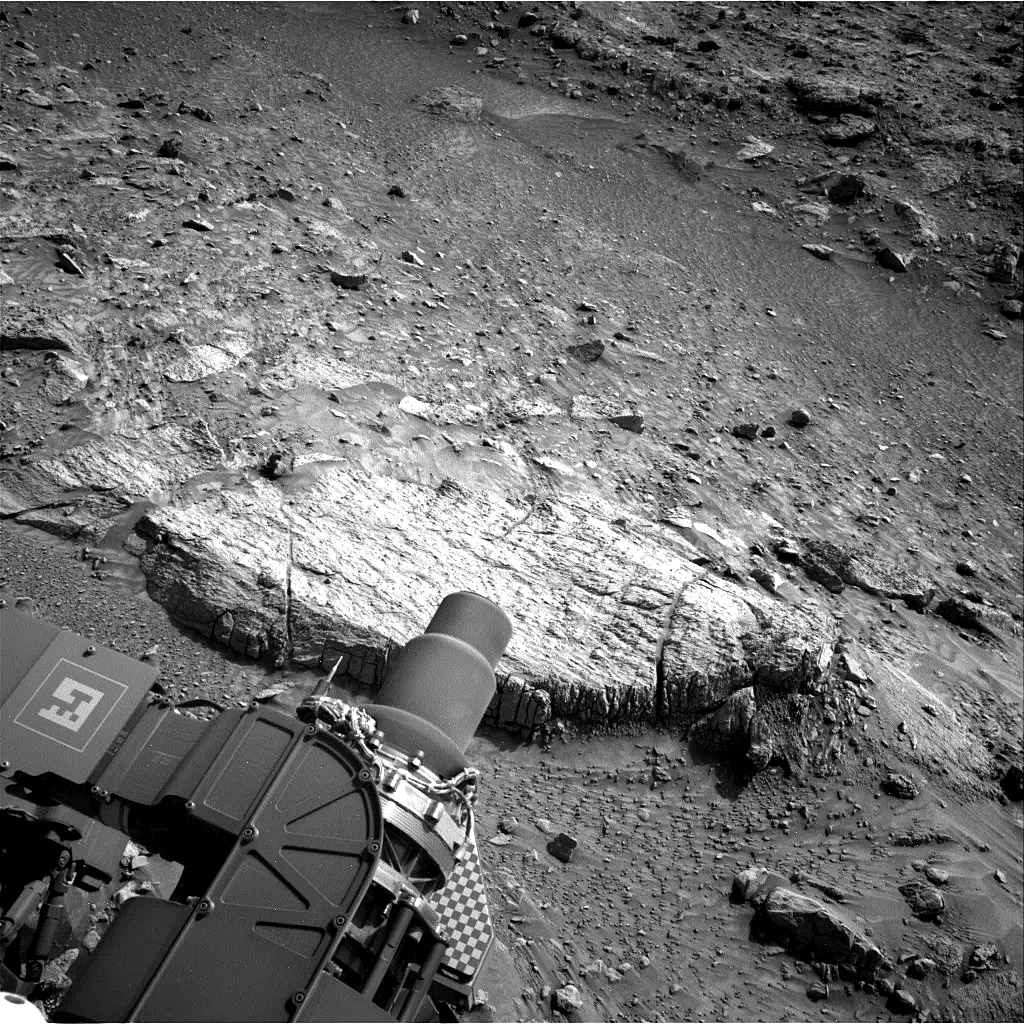
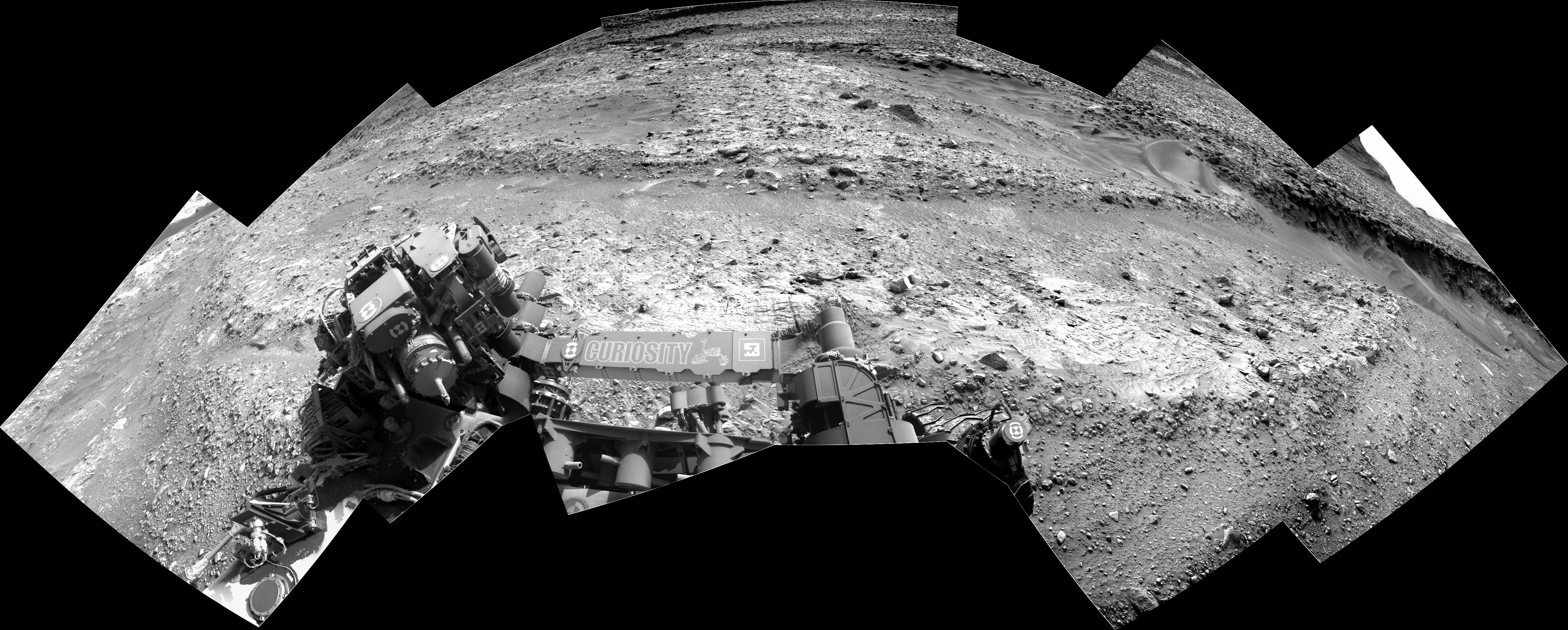
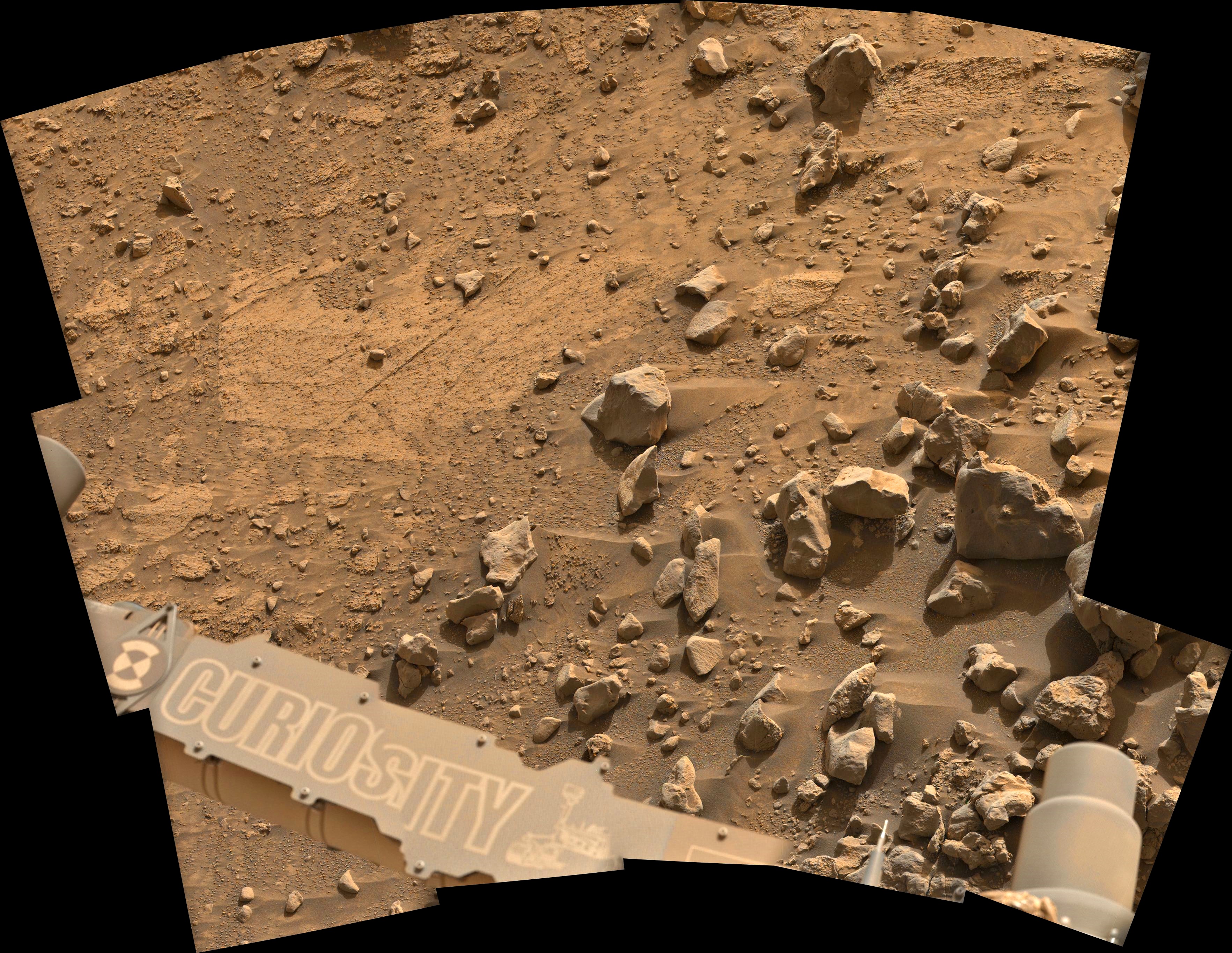
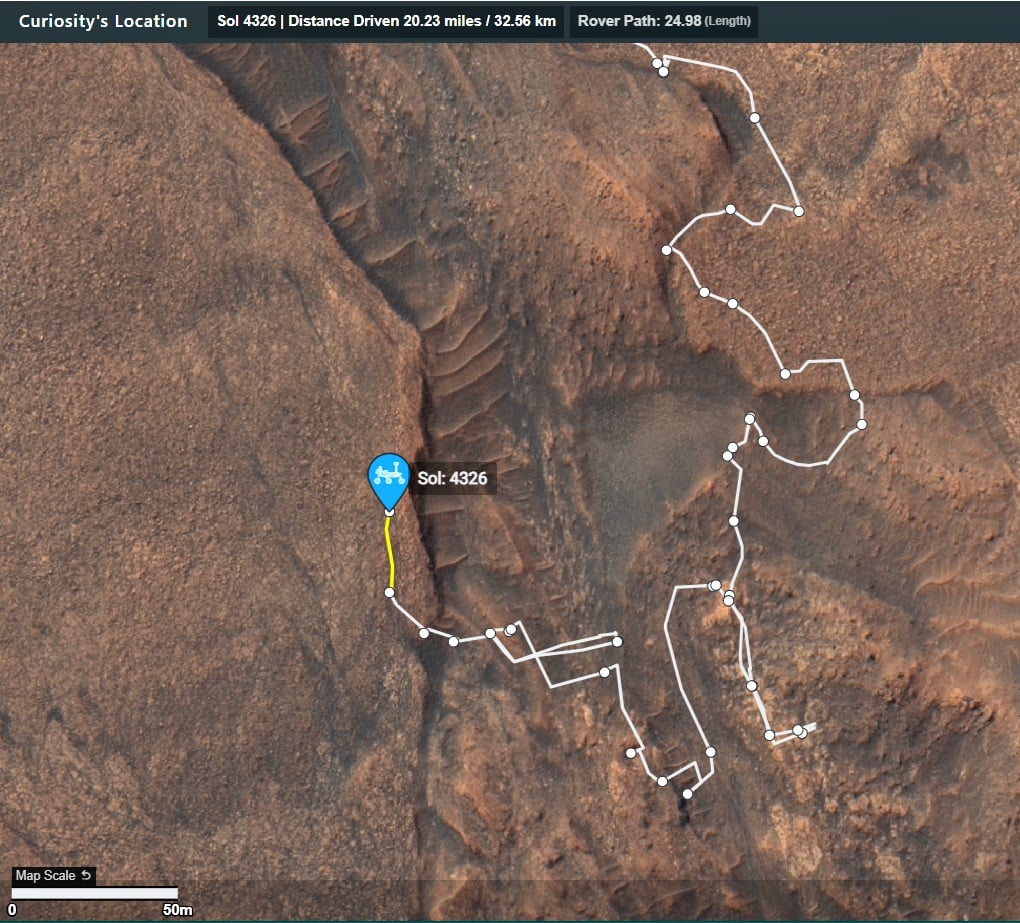
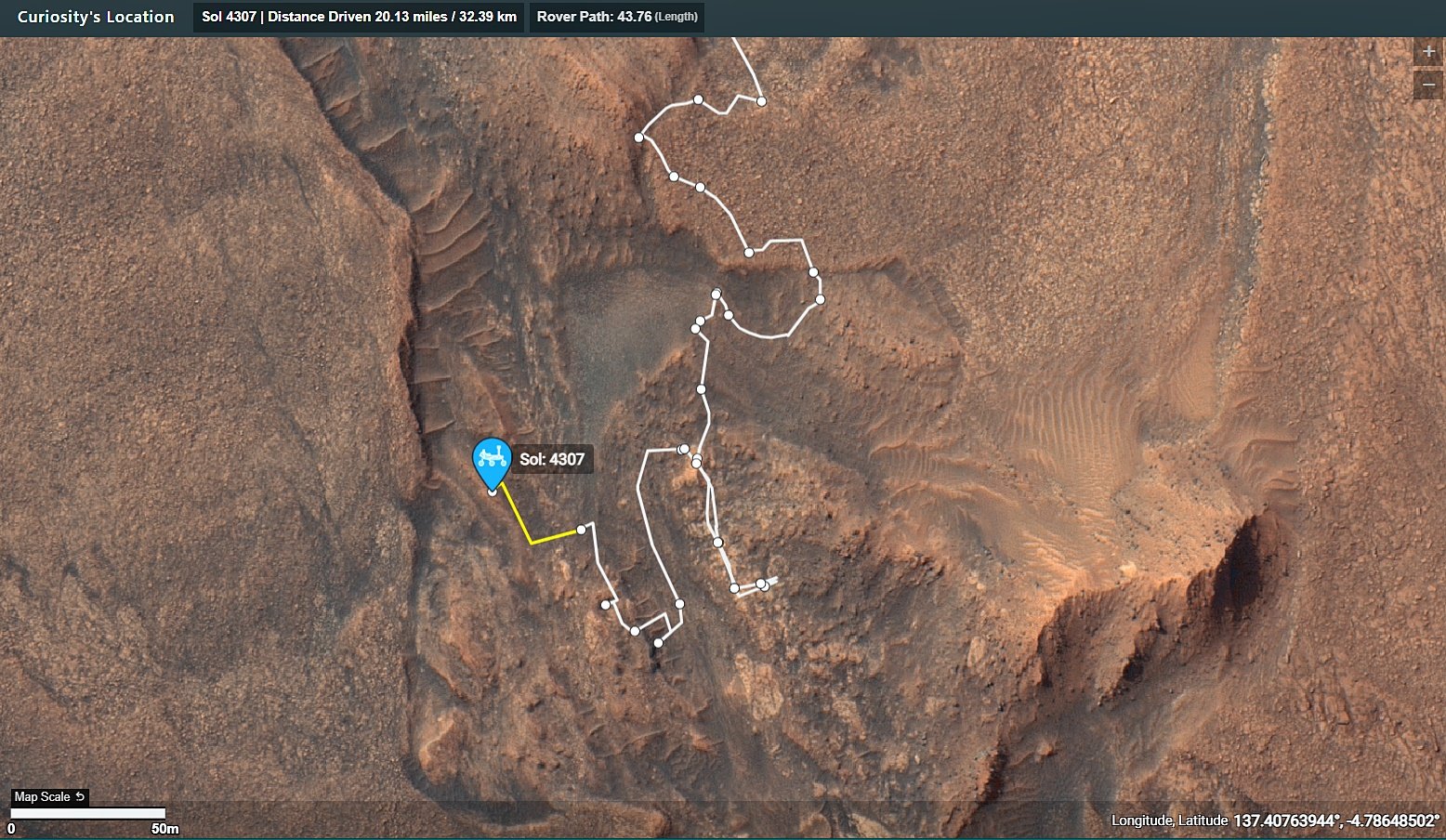
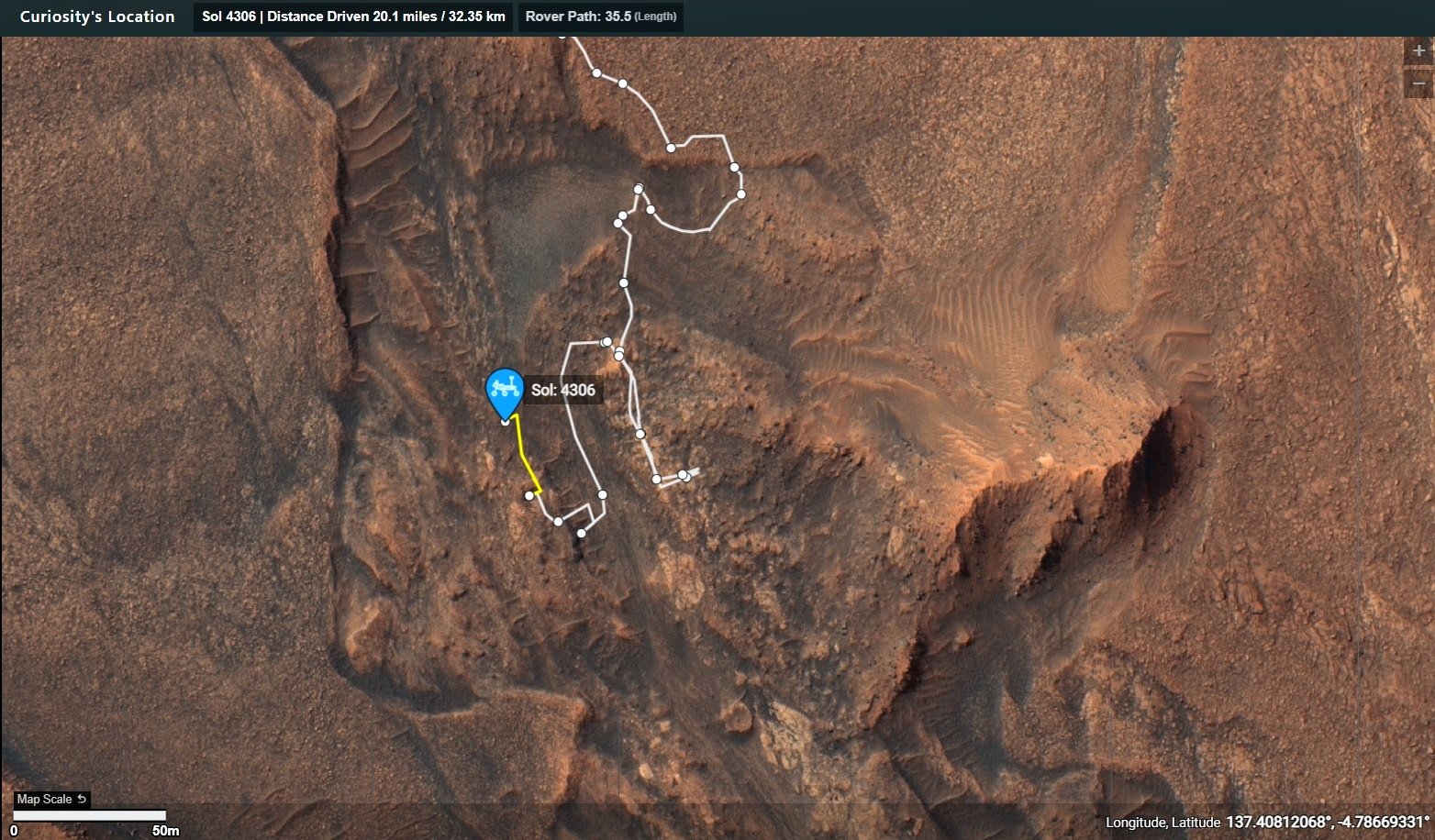
On Mars, things with our rover are going well. We completed our mega ~50-meter drive (about 164 feet) over the weekend, which took Curiosity further north along the western side of Gediz Vallis channel. Our plan today is a “touch and go,” which means we’ll do contact science with APXS and MAHLI on a block in front of us named “Dollar Lake,” some remote sensing, including ChemCam LIBS of a target named “Cape Horn” and a couple Mastcam mosaics, followed by a drive to the north. We’ll continue to follow the western side of Gediz Vallis channel as we descend slightly down Mount Sharp, until we reach a location where we are able to head west towards a more easily traversable valley, and then restart our ascent.
What a fun day of planning today. Congratulations to everyone involved helping Europa Clipper reach this incredible milestone, and go Clipper go!
Written by Abigail Fraeman, Planetary Geologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Source for this blog and the archive of all blogs (with all the links and the original raw images etc) https://science.nasa.gov/blog/sols-4334-4335-planning-with-popsicles-a-clipper-celebration/
These blog updates are provided by self-selected Mars Science Laboratory mission team members who love to share what Curiosity is doing with the public.
Dates of planned rover activities described in these reports are subject to change due to a variety of factors related to the Martian environment, communication relays and rover status.
Image credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech