this post was submitted on 14 Dec 2023
1020 points (99.2% liked)
xkcd
9146 readers
124 users here now
A community for a webcomic of romance, sarcasm, math, and language.
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
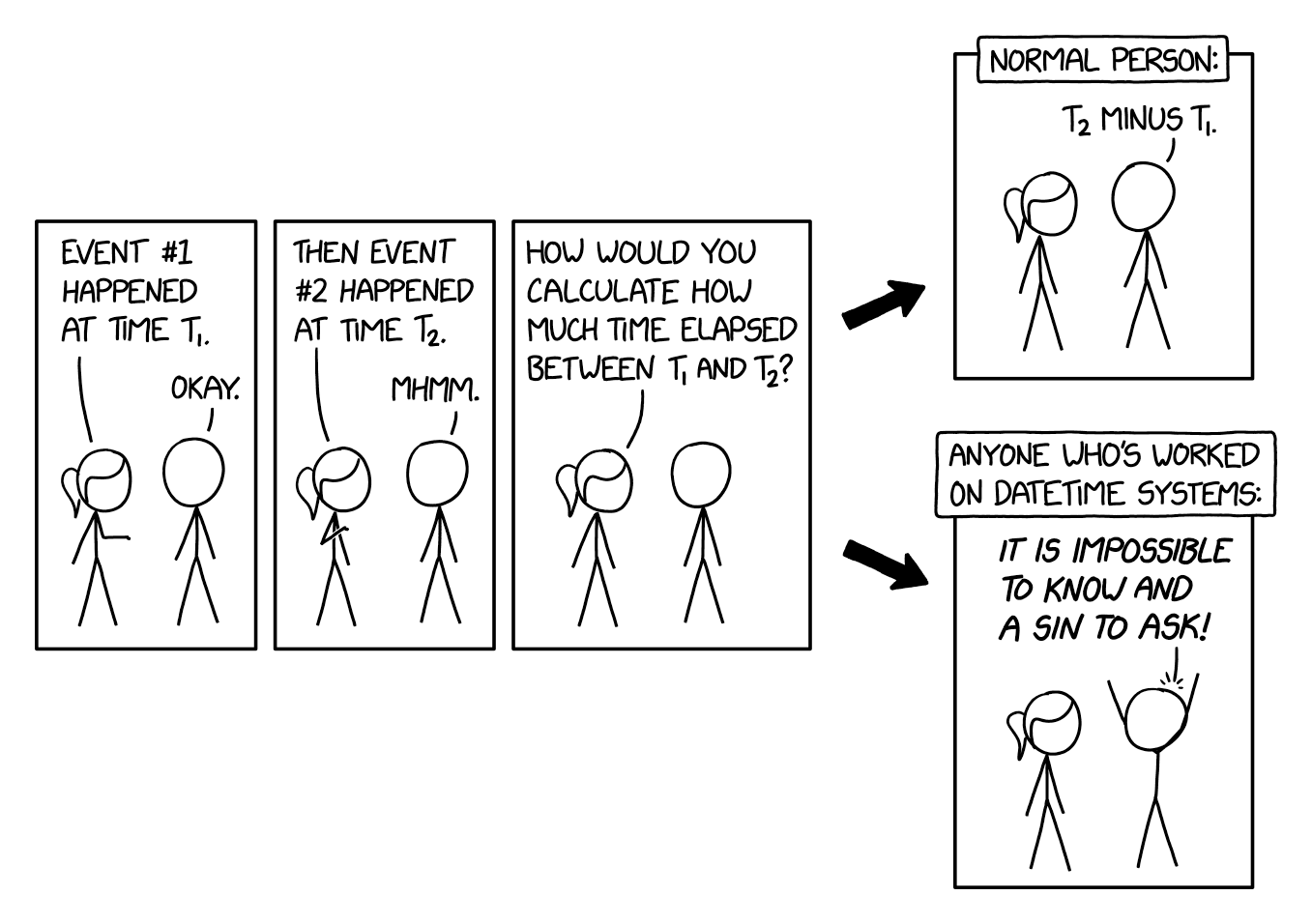
If you want one-second resolution, sure. If you want nanoseconds a 64-bit signed integer only gets you 292 years. With 128-bit integers you can get a range of over 5 billion years at zeptosecond (10^-21 second) resolution, which should be good enough for anyone. Because who doesn't need to precisely distinguish times one zeptosecond apart five billion years from now‽
If you run a realistic physical simulation of a star, and you include every subatomic particle in it, you’re going to have to use very small time increments. Computers can’t handle anywhere near that many particles yet, but mark my words, physicists of the future are going want to run this simulation as soon as we have the computer to do it. Also, the simulation should predict events billions of years in the future, so you may need to build a new time tracking system to handle that.
Good point. You'd need at least 215 bits to represent all measurably distinct times (in multiples of the Planck time, approximately 10^-43 seconds) out to the projected heat death of the universe at 100 trillion (10^14) years. That should be sufficient for even the most detailed and lengthy simulation.